Objective
To determine the clinical phenotypes associated with the β-amyloid PET and dopamine transporter imaging (123I-FP-CIT SPECT) findings in mild cognitive impairment (MCI) with the core clinical features of dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB; MCI-LB).
Methods
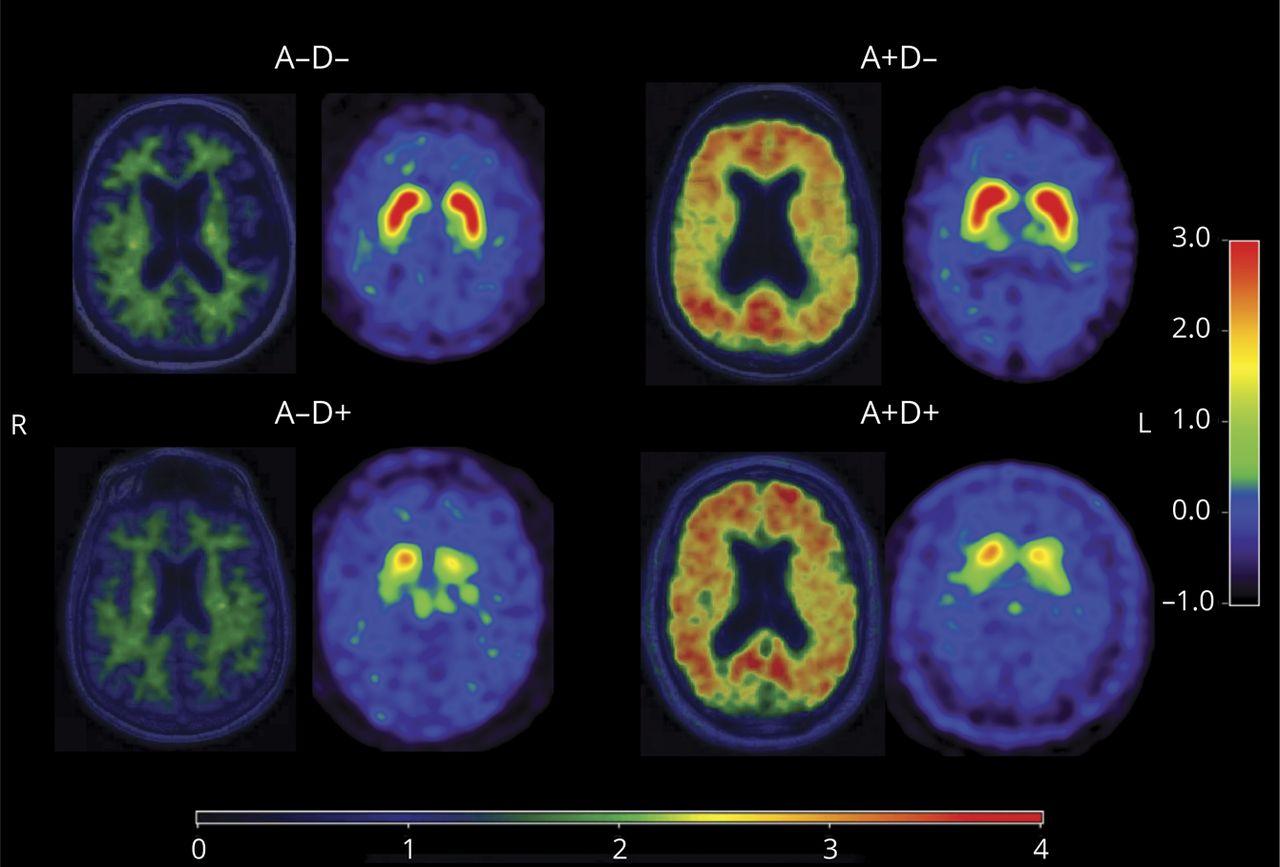
Patients with MCI who had at least 1 core clinical feature of DLB (n = 34) were grouped into β-amyloid A+ or A− and 123I-FP-CIT SPECT D+ or D− groups based on previously established abnormality cut points for A+ with Pittsburgh compound B PET standardized uptake value ratio (PiB SUVR) ≥1.48 and D+ with putamen z score with DaTQUANT <−0.82 on 123I-FP-CIT SPECT. Individual patients with MCI-LB fell into 1 of 4 groups: A+D+, A+D−, A−D+, or A−D−. Log-transformed PiB SUVR and putamen z score were tested for associations with patient characteristics.
Results
The A−D+ biomarker profile was most common (38.2%), followed by A+D+ (26.5%) and A−D− (26.5%). The least common was the A+D- biomarker profile (8.8%). The A+ group was older, had a higher frequency of APOE ε4 carriers, and had a lower Mini-Mental State Examination score than the A− group. The D+ group was more likely to have probable REM sleep behavior disorder. Lower putamen DaTQUANT z scores and lower PiB SUVRs were independently associated with higher Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale-III scores.
Conclusions
A majority of patients with MCI-LB are characterized by low β-amyloid deposition and reduced dopaminergic activity. β-Amyloid PET and 123I-FP-CIT SPECT are complementary in characterizing clinical phenotypes of patients with MCI-LB.
Source: https://n.neurology.org/content/neurology/96/8/e1180.full.pdf